j. Submit your first HPC job
The steps here can also be executed on any cluster running SLURM. There may be some variations depending on your configuration.
In this workshop, you run your first “hello world” job to introduce you to the mechanisms of AWS ParallelCluster.
Preparatory Steps
Make sure that you have your AWS Cloud9 terminal open and that you are logged into the head node.
Create the Hello World Application
First, build and compile your MPI hello world application. In your AWS Cloud9 terminal, run the following commands to create and build the hello world binary.
cat > mpi_hello_world.c << EOF
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int step, node, hostlen;
char hostname[256];
hostlen = 255;
MPI_Init(&argc,&argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &node);
MPI_Get_processor_name(hostname, &hostlen);
for (step = 1; step < 5; step++) {
printf("Hello World from Step %d on Node %d, (%s)\n", step, node, hostname);
sleep(2);
}
MPI_Finalize();
}
EOF
module load intelmpi
mpicc mpi_hello_world.c -o mpi_hello_world
If you want, you can test your application locally on the head node.
mpirun -n 4 ./mpi_hello_world
Your application is compiled and ready to be executed. Next, build a batch submission script to submit it to SLURM.
Create a Submission Script
Create submission script as shown below. This script will launch the MPI Hello World application with 4 processes and export the generated output to a *.out file.
cat > submission_script.sbatch << EOF
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=hello-world-job
#SBATCH --ntasks=4
#SBATCH --output=%x_%j.out
mpirun ./mpi_hello_world
EOF
Now, submit your fist job!
Submit your First Job
Submitted jobs are immediately processed if the job is in the queue and a sufficient number of compute nodes exist.
However, if there are not enough compute nodes to satisfy the computational requirements of the job, such as the number of cores, AWS ParallelCluster creates new instances to satisfy the requirements of the jobs sitting in the queue. However, note that you determined the minimum and maximum number of nodes when you created the cluster. If the maximum number of nodes is reached, no additional instances will be created.
Submit your first job using the following command on the head node:
sbatch submission_script.sbatch
Check the status of the queue using the command squeue. The job will be first marked as pending (PD state) because resources are being created (or in a down/drained state). If you check the EC2 Dashboard, you should see nodes booting up.
squeue
When ready and registered, your job will be processed and you will see a similar status as below.
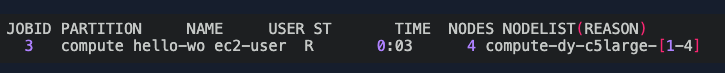
You can also check the number of nodes available in your cluster using the command sinfo. Do not hesitate to refresh it, nodes generally take less than 5 min to appear.
sinfo
The following example shows 4 nodes.

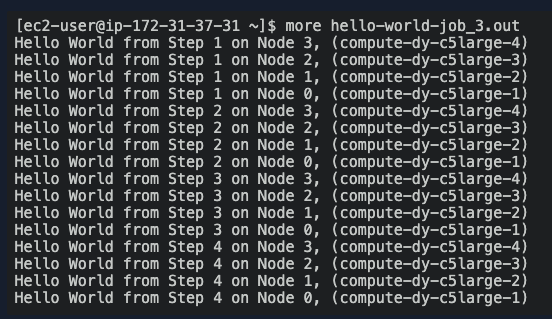
Once the job has been processed, you should see similar results as follows in the .out file:
The output is similar bellow:
Done!
After a few minutes, your cluster will scale down unless there are more job to process.