Cost controls
If you have not yet deployed a cluster, you can use the instructions for either the ParallelCluster UI or the CLI to create one. Please note the cleanup instructions at the end and include cleanup of any accounting artefacts created within this chapter - particularly if working within your own account.

In this lab, you will use Slurm Accounting within AWS ParallelCluster to create cost controls and monitor costs at the cluster level.
This lab includes the following steps:
- Configure Slurm Accounting and prerequisites
- Create cost controls using Slurm Accounting resource limits
- Test cost controls by running sample jobs
- View cluster cost data in Amazon CloudWatch
Design Overview
Cloud HPC resources have ephemeral components, such as compute nodes, that only incur cost to the user when the resources are running. Users of cloud HPC are able to leverage the cloud’s variable-cost model to cost optimize their clusters. However, the cloud’s “pay for what you use” cost model can present challenges for HPC user groups that are used to operating in a fixed-cost model. In this lab, you will implement a solution that tracks the cluster’s compute node costs and prevents jobs from running if a budget threshold is reached.
The cost control solution contains the following steps:
- Execute the cost conversion python script with the desired budget (in US dollars) as an input parameter.
- Convert the input budget to compute node CPU minutes using the AWS Price List API.
- Apply CPU minutes as a Slurm Accounting resource limit.
- Prevent Slurm job execution if the CPU minutes resource limit is reached.
Separately, you will publish cost metric data to Amazon CloudWatch to provide cost visibility in the ParallelCluster CloudWatch dashboard.
You will create the below architecture during this lab:
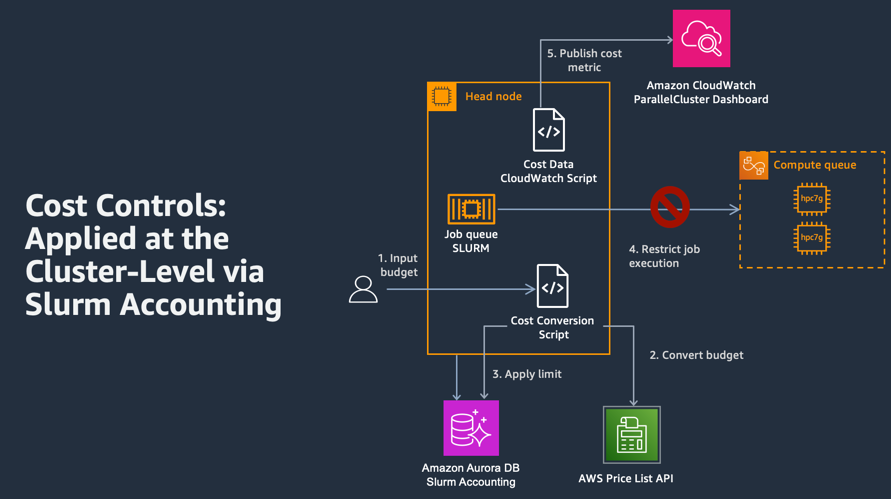
The architecture presented in this lab has the following components:
- Slurm Accounting collects accounting information for each job and job step executed. Slurm Accounting tracks resources and allows users to apply resource limits through a configuration called Group Trackable Resource Minutes (GrpTRESMins). In this lab, you will use Slurm Accounting to track compute node usage within ParallelCluster and translate usage to cost.
- Amazon Aurora is a MySQL- and PostgreSQL-compatible database built for the cloud. If taking this lab as part of a workshop an Amazon Aurora MySQL-compatible database has been pre-provisioned within your AWS sandbox account and associated with your Slurm instance via AWS ParallelCluster configuration for use with Slurm Accounting. If this is being done outside a workshop event, a database can be deployed in US East 1 Region by clicking on this button: Deploy Amazon Aurora database
- AWS Price List API provides a catalog of the products and prices for AWS services. The AWS Price List API is used in this lab to look up the dollar cost of EC2 compute node resources used by ParallelCluster.
- Cost Conversion Python script to define a cost limit in dollars, covert dollars to CPU minutes (CPUMins) using the AWS Price List API ,and apply the CPUMins value as a GrpTRESMins limit within Slurm Accounting.
- Cost Data CloudWatch Python script to publish cluster cost data to the Amazon CloudWatch service. This script extracts the total cluster compute usage from Slurm Accounting, converts usage into dollars via Price List API, and publishes the cost as a custom metric to CloudWatch.
- Amazon CloudWatch collects and visualizes real-time logs, metrics, and event data in dashboards to streamline your infrastructure and application maintenance. In this lab, you will use the Amazon CloudWatch ParallelCluster Dashboard that is created during ParallelCluster cluster creation.
Considerations and Limitations
The solution presented in this lab demonstrates the art of the possible for AWS ParallelCluster cost controls. This solution, provided as-is under the MIT license, is not intended for use in production environments. Those intending to use the concepts presented in this lab in their own environments are encouraged to build upon the capabilities demonstrated in this lab to meet their own requirements.
Capabilities that are not currently supported:
- multiple Slurm partitions (multiple ParallelCluster compute queues)
- varied compute pricing models: Spot, On-Demand, Reserved Instances, Savings Plans
- incorporating “always-on” costs including, but not limited to: head node, shared storage, networking
- handling partially used or idle compute nodes
- time-based (monthly, weekly, etc.) budgets
Documentation/Links
Some supplemental documentation is available in the AWS Docs that were used to build and develop this solution:
- Slurm accounting with AWS ParallelCluster guides users through the processes to carry out SLURM accounting; including the changes brought with AWS ParallelCluster 3.10.0 where support was included for accounting with an external Slurmdbd.
- Creating a cluster with an external Slurmdbd accounting is documentation detailing the external Slurmdbd approach. This includes a CloudFormation process to create a Slurmdbd stack.
- AWS ParallelCluster tutorial for Creating a cluster with Slurm accounting